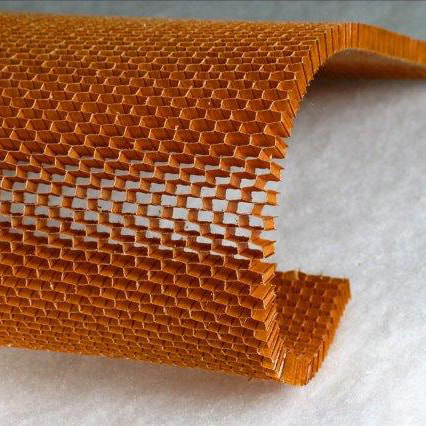
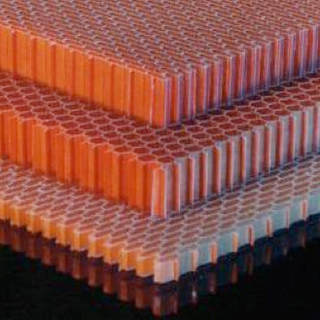
Núcleos
|
Las estructuras compuestas generalmente están diseñadas para resistir a las fuerzas en las direcciones x- y, con los refuerzos de fibra dispuestos de manera acorde. Sin embargo, cuando se aplica una fuerza en la dirección z, es decir, perpendicular a la superficie, las fibras tienen poca capacidad para resistirla.
Para tratar este problema, comúnmente se usa una estructura tipo sándwich, que consiste en dos hojas frontales de laminados compuestos tradicionales, un núcleo y materiales adhesivos para mantener la estructura unida. La función principal del núcleo es aumentar la rigidez y la resistencia a la flexión y reducir la deformación del laminado al "espesarlo". Esto puede ocasionar un aumento dramático en la rigidez para muy poco peso adicional. La conductividad térmica, el aislamiento acústico y la resistencia al fuego también se pueden mejorar con el uso de un material adecuado. Las estructuras sándwich aglomeradas han sido un elemento básico de la industria de compuestos por más de 45 años. El concepto de utilizar láminas frontales relativamente delgadas y fuertes unidas a materiales de núcleo más grueso y liviano le ha permitido a la industria construir estructuras fuertes, rígidas, livianas y altamente durables que de otro modo no se llevarían a cabo. Esta tecnología se ha demostrado en barcos, camiones, automóviles, palas de aerogeneradores y paneles de construcción. Un aumento de peso del 3% puede ampliar la resistencia a la flexión y a la rigidez en una magnitud de 3,5 veces y 7 veces, respectivamente, si los núcleos y las películas se eligen correctamente. Se encuentran disponibles diversas clases de materiales centrales, con una amplia gama de propiedades y costos: |
|
3D Glass
PET Foam
Polyurethane Foam
PVC Foams
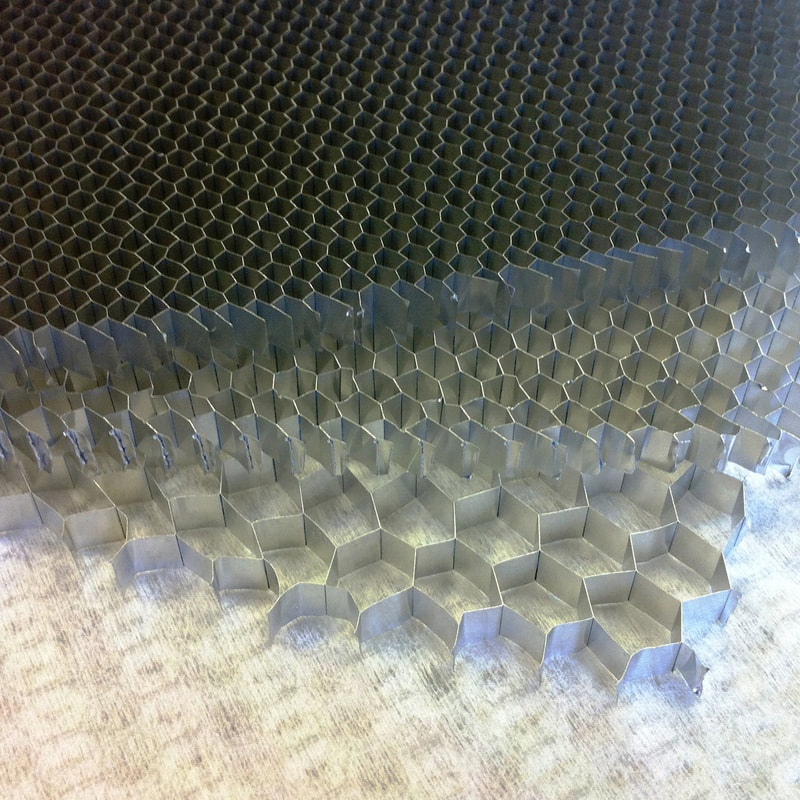
Honeycomb
Nomex®
Aluminium honeycomb
|